Le modèle d'apprentissage automatique, GPT-1 ou Generative Pre-training Transformer 1, est une création de l'OpenAI, spécialement conçue pour la compréhension et la génération de tâches de langage humain. Il se caractérise par une structure de transformateur à 12 couches, décodeur uniquement, équipée de douze têtes d'auto-attention masquées à 64 dimensions. L'optimisation des performances de GPT-1 est réalisée à l'aide de l'optimisation Adam algorithme[1]qui se caractérise par un taux d'apprentissage croissant de manière linéaire. Avec un nombre remarquable de 117 millions de paramètres, le GPT-1 met en évidence sa conception complexe. Malgré sa structure avancée, des ajustements minimaux sont nécessaires lorsqu'il est déployé pour différentes tâches. Ses compétences sont particulièrement évidentes dans le domaine du langage naturel déduction[2] Il s'agit d'un modèle qui permet d'effectuer des tâches de recherche, de réponse à des questions, de raisonnement par le bon sens et de similarité sémantique. L'une des ressources clés de ce modèle est l'ensemble de données BookCorpus, choisi pour ses longs passages qui facilitent la gestion d'informations à long terme.
Cet article peut s'appuyer de manière excessive sur des sources un lien trop étroit avec le sujetL'article n'a pas été publié, ce qui pourrait empêcher l'article d'être publié. vérifiable et neutre. (Août 2023) |
Transformateur génératif pré-entraîné 1 (GPT-1) a été le premier des OpenAI's grands modèles linguistiques suivants GoogleL'invention de la transformateur en 2017. En juin 2018, OpenAI a publié un document intitulé "Improving Language Understanding by Generative Pre-Training", dans lequel elle présente ce modèle initial ainsi que le concept général d'un modèle d'apprentissage génératif (Generative Pre-Training). transformateur génératif pré-entraîné.
| Auteur(s) original(aux) | OpenAI |
|---|---|
| Version initiale | Juin 2018 |
| Référentiel | |
| Successeur | GPT-2 |
| Type | |
| Licence | MIT |
| Site web | openai |
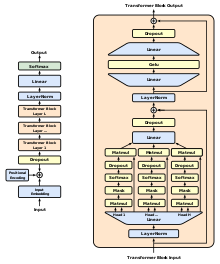
Jusqu'à présent, les modèles neuronaux de NLP les plus performants utilisaient principalement les éléments suivants apprentissage supervisé à partir de grandes quantités de données étiquetées manuellement. Cette dépendance à l'égard de l'apprentissage supervisé a limité leur utilisation d'ensembles de données qui n'étaient pas bien annotés, en plus de rendre prohibitif le coût et le temps nécessaires pour former des modèles de très grande taille ; de nombreuses langues (telles que le Swahili ou Créole haïtien) sont difficiles à traduire et à interpréter à l'aide de tels modèles en raison du manque de textes disponibles pour la constitution de corpus. En revanche, l'approche "semi-supervisée" d'un TPG comporte deux étapes : une approche non supervisée et une approche "semi-supervisée". génératif une phase de "pré-entraînement" au cours de laquelle un objectif de modélisation linguistique a été utilisé pour définir les paramètres initiaux, et une phase d'entraînement supervisé, au cours de laquelle un objectif de modélisation linguistique a été défini. discriminatoire une phase de "réglage fin" au cours de laquelle ces paramètres sont adaptés à une tâche cible.
L'utilisation d'un transformateur Contrairement aux techniques précédentes impliquant des RNNs augmentés par l'attention, l'architecture de la GPT avec une mémoire plus structurée que celle qui pourrait être obtenue par des mécanismes récurrents, ce qui a permis d'obtenir des "performances de transfert robustes dans diverses tâches".